Hair growth through transplantation surgery also known as hair restoration is one of the most valuable and exciting surgical treatments for male pattern androgenic baldness and other causes of hair loss in the field of aesthetic surgery nowadays. Medical treatments with finasteride and minoxidil both are used in management of pattern baldness but the results are quite not satisfactory and are often temporary. And thus, surgical treatment remains the mainstay of treatment. With newly developed methods of harvesting and implanting follicles, this treatment has been much better and truly depicts an amalgam of art and science.
Hair growth is dependent on multiple factors and the most important one is the male hormone testosterone that is converted to 5- dihydrotestosterone in the roots of the follicles. In genetically predisposed individuals, due to the effect of 5-dihydrotestosterone, follicles at the top and front of the scalp become more and more fine as the years pass. Eventually with time the growth gets limited and the hair completely disappears. In women, however, the front hairline is usually not affected and baldness in females has a separate classification.
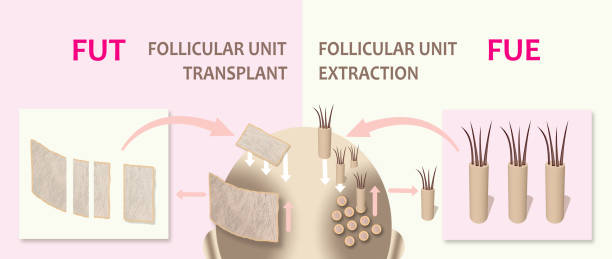
Hair transplantation basically stems from our understanding of “theory of donor dominance and androgenic alopecia”. Grafts are usually taken from the area that is permanently destined to be hair bearing and are transplanted over areas suffering from male pattern baldness. Follicular graft unit (FUG) includes 1 to 4 terminal follicles, 1 vellus follicles, arrector pili muscle insertion, sebaceous lobules, perifollicular neurovascular network. Thus, the follicle should be considered as a physiological unit rather than an anatomical one. It is practically more reassuring to describe a follicular unit as a group of hair shafts arising from the scalp with the distance between hairs less than the distance to the closed aggregation of hair. This pattern gives the best efficacy and most natural appearance to the patient.

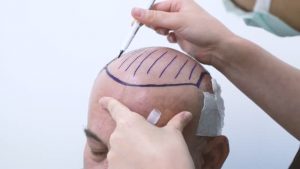
While planning a transplant, the most important step is to create a natural hairline, which varies from person to person depending on the shape of the face of the patient. Transplantation is done from the donor site to the recipient site and the patient is usually discharged on the same day, usually with no bandage. There may be some swelling after the transplant surgery and the patient should be informed about this before the procedure. Per oral steroids are given for a few days to minimize the swelling. Patients should wash their scalp very gently with a mild shampoo after 3 to 5 days of surgery. 5% minoxidil lotion should be applied to the transplanted area as recommended by the surgeon. Care should be taken regarding wearing pull over clothes or anything that has to be taken off over the head, these should be avoided in the initial postoperative period. Scalp oils and strong shampoos should be avoided and only medicated and prescribed products should be used. New hairs start growing after about 3 months postoperative period and it takes about six to nine months to notice some appreciable effects of transplantation. The density of hair in the totally bald areas is thinner post operatively and a 2nd procedure may be necessary to increase the density of hair. If a second procedure is required, it should be planned 3-6 months after the initial surgery. Although transplant has great results given proper preoperative, operative and postoperative preparations are made, it may result in some complications. Patients may complain of hypoesthesia i.e., decreased sensation on the scalp at the donor site, however it is temporary and usually persists only for about 18 months in most patients. There may be infection at the donor or the recipient site. Overall, transplantation is a revolutionary step in the treatment of hair loss and judicious use and with expert care, it can prove life changing for the patient.